- App Inventor 2 Download Windows
- App Inventor Download Windows 10
- App Inventor 2 Ultimate Download
- Download App Inventor Full
- App Inventor 2 Download Mac Os
- App Inventor 2 Download Mac Installer
App inventor 2 ultimate free download. App Inventor 2 Ultimate All in one App Inventor 2 offline server environment. From original project MIT App Inventor: https. Download App Inventor 1.1 for Mac from our software library for free. This Mac download was scanned by our antivirus and was rated as safe. The latest installation package takes up 87.9 MB on disk. The program lies within Developer Tools, more precisely IDE. The actual developer of this free software for Mac is Google Labs. App inventor 2 templates free download - App Inventor 2 Tutorials FREE, App Inventor, KGB Archiver 2, and many more programs. Enter to Search. My Profile Logout.
Help yourself to faster programming by purchasing my App Inventor 2 Guides from any of the following vendors – thank you very much!
Detailed descriptions of all the books are below, including Table of Contents and some sample chapters.
- Download app inventor for free. Internet & Network downloads - MIT App Inventor by Appinventor mit edu and many more programs are available for instant and free download.
- Students will learn about MIT app inventor 2 while they create an actual translator app. Anyone who can use a computer can take this course. If you ever wanted to know how you can create your own translator app then, you are at the right place.
Where to Buy
- App Inventor 2 Introduction (Volume 1 e-book)
Step-by-step guide to easy Android programming
Buy from: Amazon, Google Books, Kobo Books, Apple iBooks - App Inventor 2 Advanced Concepts (Volume 2 e-book)
Step-by-step guide to Advanced features including TinyDB
Buy from: Amazon, Google Books, Kobo Books - App Inventor 2 Databases and Files(Volume 3 e-book)
Step-by-step TinyDB, TinyWebDB, Fusion Tables and Files
Buy from: Amazon, Google Books, Kobo Books - App Inventor 2 Graphics, Animation and Charts (Volume 4 e-book and printed book)
Step-by-step guide to graphics, animation and charts
Buy e-book from: Amazon, Google Books, Kobo Books - Price: US$5.99 (e-book), US$12.99 (printed book, 227 pages)
- The print version of Volume 4 has been discontinued due to rampant online theft of the product.
How to Read
While the e-books can be read on e-book reader devices[1], I recommend using the free e-reader software available from each e-book distributor for reading on your notebook or desktop computer:
- Your Amazon e-book library may be read online, through a browser, here.
- Kobo e-reader app for Windows, Android, iOS
- Google Books may be read in a web browser, or using the Google Play Books app on Android and iPad/iPhone.
Note [1] – images used in the e-books do not always display well on the e-book reader devices (e.g. Kindle). For this reason, use of computer-based e-book reader software is recommended.
Covers
Download Sample Chapter: App_Inventor_2_Introduction_Chap4.pdf
Where to Buy
Volume 1 – Description
MIT App Inventor 2 is the fast and easy way to create custom Android apps for smart phones or tablets. This guide introduces the basic App Inventor features – you can likely create your first simple app in an hour, and understand the basic components of App Inventor in a full day. App Inventor 2 is free to use and you can use it for commercial applications too.
App Inventor 2: Introduction is targeted at adult learners (high school and up) and shows how to design your app’s user interface with “drag and drop” interface controls to layout your app’s screen design. Then implement the app’s behavior with unique “drag and drop” programming blocks to quickly assemble the program in a graphical interface.
This tutorial covers the basics of the App Inventor user interface Designer and the Blocks programming editor, plus basic “blocks” programming concepts and tools for arithmetic, text processing, event handling, lists and other features.
INTRODUCTION
WHAT THIS GUIDE COVERS
ORGANIZATION OF THIS GUIDE
Tip – Learning to Program
RECOMMENDATION
SOURCE CODE DOWNLOAD
ACCESSING MIT APP INVENTOR
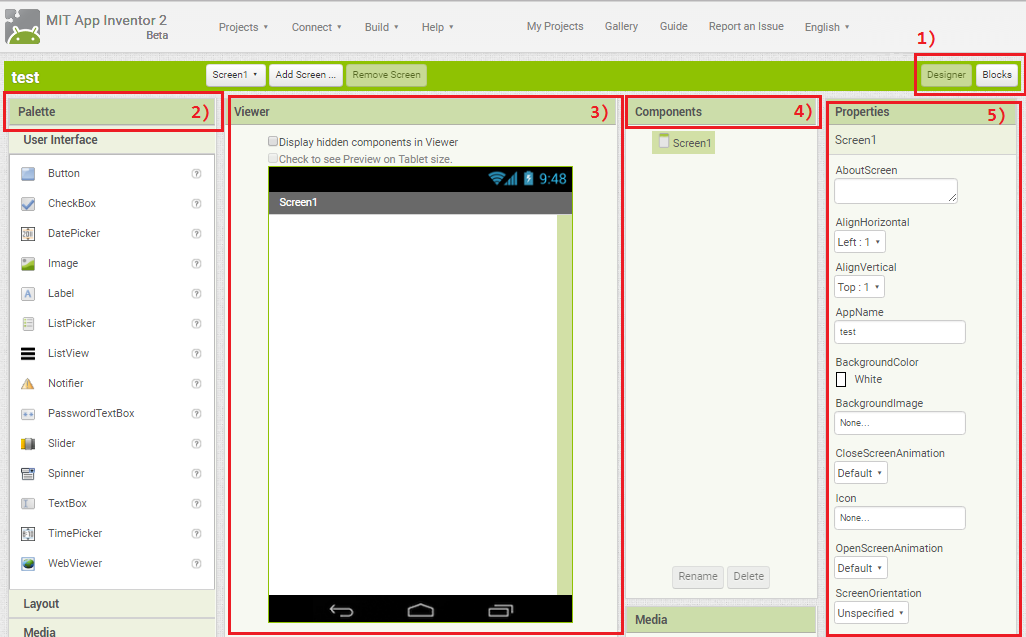
INTRODUCTION TO THE DESIGNER
INTRODUCTION TO THE BLOCKS EDITOR
PROGRAMMING THE APP’S BEHAVIOR
Tip – Events and Event Handlers
THE BUTTON EVENT HANDLER
TIP – AI2.APPINVENTOR.MIT.EDU
ORGANIZATION OF THIS GUIDE
SUMMARY
PRACTICE
1 – RUNNING APPS ON YOUR ANDROID PHONE
Tip – Where to Get an Android Phone
WI-FI METHOD FOR INSTALLING APPS
Tip – Automatic Real Time Code Updates
USB METHOD
ANDROID APPLICATION FILE DOWNLOAD
Building the .apk file
USING THE EMULATOR
SAVING AND LOADING SOURCE CODE
Loading .aia Source Code Files
SAVING .AIA SOURCE CODE FILES
SUMMARY
PRACTICE
2 – BUILDING A CALCULATOR APP USER INTERFACE
THE IMPORTANCE OF LAYOUTS
ADD A TABLE LAYOUT
SUMMARY
PRACTICE
3 – BUILDING THE CALCULATOR BLOCKS PROGRAM
CONCEPT OF CALCULATOR OPERATION
INTRODUCTION TO VARIABLES
Tip – Why is it called global instead of variable?
BLOCKS FOR IMPLEMENTING CALCULATOR KEYS
ADDING COMMENTS
IMPLEMENTING THE ARITHMETIC FUNCTIONS
PERFORMING THE ARITHMETIC OPERATION
RUN THE PROGRAM
SUMMARY
PRACTICE
4 – LAYOUTS IN DETAIL
THE VERTICAL LAYOUT
THE HORIZONTAL LAYOUT
NESTED LAYOUTS
LAYOUT SCREEN SIZE AND SCROLLING
TIP – CONSIDER AVOIDING “LONG” SCREENS
RESTRICTIONS ON LAYOUTS
Restriction on Screen Complexity
SUMMARY
PRACTICE
5 – APPS WITH MULTIPLE SCREENS
THE BOAT RENTAL APPLICATION
ADDING ADDITIONAL “SCREENS”
BLOCKS CODE TO SWITCH SCREENS
NEWCUSTOMER BLOCKS CODE
EXCHANGING VALUES BETWEEN SCREENS
RETURNING A VALUE FROM A SCREEN
RETRIEVING THE RETURNED VALUE IN THE CALLING SCREEN
“PARAMETERS”
HANDLING MULTIPLE SCREENS WITH RETURN VALUES
Using if-then-else blocks
Setting a Condition in the if-then Block
SUMMARY
PRACTICE
6 – INTRODUCTION TO TEXT
UPCASE AND DOWNCASE
JOIN – JOINING TEXT ITEMS TOGETHER
TEXT LENGTH
ISEMPTY
COMPARE TEXTS
TRIM TEXT FUNCTION
CHECKING THE CONTENT OF STRINGS
TEXT PROCESSING IN PRACTICE
EXTRACTING STRING SEGMENTS FROM TEXT
SUMMARY
PRACTICE
7 – ARITHMETIC IN APP INVENTOR
ARITHMETIC ORDER OF CALCULATIONS
TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
SQUARE ROOT AND OTHER MATH FUNCTIONS
RANDOM NUMBER GENERATORS
SUMMARY
PRACTICE
8 – INTRODUCTION TO LISTS
CREATE
SEARCHING THE LIST
COMBINING LISTS
Local Grocer
Warehouse Store
OUTPUT A LIST TO THE SCREEN
CONVERTING LISTS TO COMMA SEPARATED VALUES
LISTS OF LISTS
SEARCHING A LIST OF LISTS
USING LOOKUP IN PAIRS
INTRODUCING FOREACH
TIP – CREATE, READ, UPDATE, DELETE
USING LIST TO CSV TABLE CONVERSION
OTHER LIST BLOCKS
Copy list
SUMMARY
PRACTICE
9 – ADVANCED TEXT FUNCTIONS
ADDITIONAL SPLIT FUNCTIONS
SUMMARY
PRACTICE
10 – MAKING CODE RUN MULTIPLE TIMES
USING THE FOR EACH FROM TO LOOP
LOCAL VARIABLES
WHY USE LOCAL VARIABLES?
INTRODUCTION TO THE FOR EACH LOOP
Tip – The “by” value may be negative
FAHRENHEIT TO CELSIUS CONVERSION TABLE APP
WHILE DO LOOP
SUMMARY
PRACTICE
Download sample chapter: App_Inventor_2_Advanced_Concepts_Chap1.pdf
Where to Buy
Volume 2 – Description
MIT App Inventor 2 is a fast and simple way to create custom Android apps for smart phones or tablets. Volume 2 in the series introduces debugging methods, explains additional controls not covered in Volume 1, introduces “agile” methods for developing a real world app, and provides sample code for using the TinyDB database.
The App Inventor 2 Tutorial series is targeted at adult learners (high school and up). App Inventor 2 provides a simplified “drag and drop” interface to layout your app’s screen design. Then implement the app’s behavior with “drag and drop” programming blocks to quickly assemble a program in a graphical interface.
Volume 1 of this series covered the basics of the App Inventor user interface Designer and the Blocks programming editor, plus basic “blocks” programming concepts and tools for arithmetic, text processing, event handling, lists and other features. Volume 2 builds upon Volume 1 to provide tips on debugging programs when the apps work incorrectly, how to us hidden editing features, and how to install your own apps on to your phone or tablet for general use. Code samples are provided for using the Notifier component for general use or for debugging, for user interface control tricks such as buttons that change color continuously or implementing the missing “radio buttons” component, using ListPicker and Spinner for list selections, and using the WebViewer to display web pages in your app. The book includes a large section on designing and building a sample real world application and finishes with a chapter on using the TinyDB database.
For readers of the blog, Chapters 4–8 are based on the tutorial already presented here. Chapter 2 and Chapter 9 on TinyDB are all new material.
Chapters
- Introduction
- 1 – App Inventor Tips
- 2 – Debugging App Inventor Programs
- 3 – User Interface Control Tricks
- 4 – Designing and Building a Real World Application
- 5 – Tip Calculator Version 2
- 6 – Tip Calculator Version 3
- 7 – Tip Calculator Version 4
- 8 – Tip Calculator Version 5
- 9 – Using the TinyDB database
App Inventor 2: Advanced Concepts
About the Author
Table of Contents
Introduction
Conventions
1 – App Inventor Tips
Cut, Copy and Paste within the App Inventor Blocks Editor
Windows
Mac OS X
Duplicating Blocks in the Blocks Editor
Windows
Mac OS X
Re-arranging, Collapsing and Zooming the Blocks View
Bonus Tip!
Backing Up: Saving App Projects to Your Computer
Backing Up: Use “Checkpoint” to save periodic “snap shots” of your project
Installing Apps on Your Phone
Building an App Using the QR Code Method
Where is the downloaded .apk file?
Download an App for Installation
Using App Inventor’s Official Documentation
Events
Properties
Methods
Back to the Documentation
2 – Debugging App Inventor Programs
Debugging
Overview
User input errors
Divide by zero errors
Off by 1 errors
Logic errors
Basic Strategies for Debugging
Review of Basic Debugging Techniques
Real Time Program Editing
Using Notifier to Alert the User to Problems
Adding a Progress Indicator to Notifier
Sample Program User Interface
Designer View
Blocks Code
3 – User Interface Control Tricks
Buttons: Changing Colors and Attributes
Designer View
Blocks Code
Implement Continuously Changing Control Colors
Designer View
Blocks Code
Hiding the Text Entry Keyboard
Radio Buttons
Designer View
Blocks Code
ListPicker
Using ListPicker
Building the ListPicker Sample Application
Tip – Find Out More About Lists
Using ListPicker Filters
Designer View
Blocks Code
Spinner
Designer View
Blocks Code
Changing the Spinner Choices Programmatically
Designer View
Blocks Code
WebViewer
Designer View
Blocks Code
4 – Designing and Building a Real World Application
Tip – Software Design and Agility
The Five Versions
Tip Calculator Version 1
The Tip Calculator User Interface
Blocks Code
How This Works
5 – Tip Calculator Version 2
The Tip Calculator User Interface
Blocks Code
6 – Tip Calculator Version 3
Designer View
Blocks Code
7 – Tip Calculator Version 4
Blocks Code
Key Features Shown
Tip – Refactoring and Software Testing
8 – Tip Calculator Version 5
The Tip Calculator User Interface
Designer View
Blocks Code
Summary of Versions 1 through 5
9 – Using the TinyDB database
Introduction to Databases
Terminology: TinyDB Versus Databases
TinyDB – Create, Retrieve, Update, Delete – and Search
Using the Task List App
Add Tasks
Delete Item
Search by Content
Clear All Tasks
Designer View: Screen1
Blocks Code: Screen1
Designer View: Add Item
Blocks Code: Add Item
Designer View: Edit Item
Blocks Code: Edit Item
Designer View: List Tasks
Blocks Code: List Tasks
Designer View: Search by Content
Blocks Code: Search by Content
Download sample chapter: App_Inventor_2_Databases_Chap1.pdf
Where to Buy
Volume 3 Description
App Inventor 2: Databases and Files is a step-by-step guide to writing apps that use TinyDB, TinyWebDB, Fusion Tables and data files for information storage and retrieval. Includes detailed explanations, examples, and a link to download sample code. This is the first tutorial to cover all of these App Inventor database and file features.
If your apps need to work with data or files – you need this book!
TinyDB stores data on your smart phone or tablet and is a primary way for App Inventor apps to save data, even when the app is no longer running or if the device is turned off.
TinyWebDB is similar to TinyDB, but stores your data on a remote server in the network cloud.
Multiple apps can share a TinyWebDB database, plus you can update the content of your TinyWebDB using just a web browser. This means you can distribute an app whose content can change over time – just by changing the values in TinyWebDB.
A big challenge is the need to set up a TinyWebDB server – this book shows how to do that through free services offered by Google.
Fusion Tables provide a powerful, cloud-based database system for App Inventor apps. Creating, retrieving, updating and deleting data is done using the industry standard Structured Query Language or SQL. Fusion Tables reside in the Google network cloud – this book shows you how to set up and configure Fusion Tables for you own apps using free services of Google. As your app requirements grow, Google’s cloud can provide low cost servers and bandwidth for your needs.
Underneath the Android OS user interface, there is a file system, similar to the file system found on Windows or Mac OS X. With App Inventor your apps can write and read data from files, and if using the special “CSV” format, App Inventor data can be shared with many spreadsheet programs. This book shows you how to create, use and access data files, and how to convert data to and from the CSV format.
Over 28,000 words. Over 250 screen shots and illustrations. Numerous sample programs and code. Amazon’s page count is 322 pages.
The link to the App Inventor source code download files is on “the copyright” page – about page 2 or 3 – in your e-reader version.
Updates and “errata” to the e-books are located on this page.
Chapters
- 1 – Introduction
- 2 – Using the TinyDB database
- 3 – Implementing Records Using Lists in TinyDB
- 4 – Simulating Multiple TinyDB Databases
- 5 – How to Use Multiple Tags in TinyDB
- 6 – Introduction and Setup: TinyWebDB
- 7 – Managing TinyWebDB in the Cloud
- 8 – Programming for TinyWebDB – Demo 1
- 9 – Adding a Tags List to TinyWebDB – Demo 2
- 10 – Handling Multiple Users with TinyWebDB – Demo 3
- 11 – Implementing a Student Quiz Application using TinyWebDB
- 12 – Introduction to Fusion Tables
- 13 – Developing Your Fusion Table App
- 14 – Using Text Files in App Inventor
Detailed Table of Contents
1 – Introduction
TinyDB
TinyWebDB
Fusion Tables
Which database component to use?
Choosing Which Database to Use
TinyDB
TinyWebDB
Fusion Tables
Text Files
Conventions
About the Sample Apps
2 – Using the TinyDB database
Introduction to Databases
Terminology: TinyDB Versus Databases
TinyDB – Create, Retrieve, Update, Delete – and Search
Source Code
Using the Task List App
Add Tasks
Delete Item
Search by Content
Clear All Tasks
Designer View: Screen1
Blocks Code: Screen1
Designer View: Add Item
Blocks Code: Add Item
Designer View: Edit Item
Blocks Code: Edit Item
Designer View: List Tasks
Blocks Code: List Tasks
Designer View: Search by Content
Blocks Code: Search by Content
3 – Implementing Records Using Lists in TinyDB
Source Code
The User Interface
Designer View: Screen1
Blocks Code: Screen1
Designer View: AddItem
Blocks Code: AddItem
Designer View: ListTasks
Blocks Code: ListTasks
Designer View: Delete
Blocks Code: Delete
Designer View: Search by Content
Blocks Code: Search by Content
Designer View: Edit Contact
Blocks Code: Edit Contact
4 – Simulating Multiple TinyDB Databases
Source Code
Designer View: Screen1
Blocks Code: Screen1
IMPORTANT NOTE
Designer View: AddItem
Blocks Code: AddItem
Designer View: ListTasks
Blocks Code: ListTasks
Designer View: Search
Blocks Code: Search
5 – How to Use Multiple Tags in TinyDB
Source Code
Designer View: Screen1
Blocks Code: Screen1
Designer View: AddItem
Blocks Code: AddItem
Designer View: Delete
Blocks Code: Delete
Designer View: List Contacts
Blocks Code: List Contacts
Designer View: Edit
Blocks Code: Edit
Designer View: Search by Content
Blocks Code: Search by Content
Designer View: Select by Employee ID
Blocks Code: Select by Employee ID
Designer View: Select by Name
Blocks Code: Select by Name
Designer View: Admin
Blocks Code: Admin
6 – Introduction and Setup: TinyWebDB
Setting Up Your Own TinyWebDB Service
Setting Up TinyWebDB in the Google Cloud
Installation Steps (Short version)
Overview
Short Version
Installation Instructions (Long version)
Step 1 – Install Python
Step 2 – Install Google App Engine Launcher
Step 3 – Download customtinywebdb.zip
Step 4 – Set up Google Account
Step 5 – Run Google App Engine Launcher
Step 6 – Return to Google App Engine Launcher
Important Steps
Step 7 – Return to the App Engine Launcher program.
Step 8 – Quick Test
Problems
7 – Managing TinyWebDB in the Cloud
Use the TinyWebDB Web Interface to Get and Store Values
Management of the Database
Tip – Enabling Datastore Admin Features
Selecting your database
Delete individual records in the TinyWebDB Database
Delete the content of a database
Deleting a Project
8 – Programming for TinyWebDB – Demo 1
Source Code
The User Interface
Designer View
Blocks Code
TinyDB: Synchronous Operation
TinyWebDB: Asynchronous Operation
9 – Adding a Tags List to TinyWebDB – Demo 2
Source Code
The User Interface
Designer View
Blocks Code
Simple Explanation of GotValue
Processing Multiple Pending GetValue Requests in GotValue
10 – Handling Multiple Users with TinyWebDB – Demo 3
Deadlocks
Source Code
The User Interface
Designer View
Blocks Code
Timer Operation
Timer Event Tags Management
11 – Implementing a Student Quiz Application using TinyWebDB
Source Code
The User Interface
Database View
Setting up the Questions Database
Designer View: Screen1
Blocks Code: Screen1
Designer View: DoQuiz
Blocks Code: DoQuiz
12 – Introduction to Fusion Tables
What is a Fusion Table?
Setting Up a Fusion Table Service
Tip – Keep Track of Key Data As You Create Tables
Key Steps
Create Your Fusion Table
Define the Table Layout
Gather the Table ID
Sharing Your Table
Creating a Google Group for Sharing [Optional Step]
One More Group Step!
Generating an API Key For Your App Access
13 – Developing Your Fusion Table App
CREATE
“Forbidden” Message?
READ
DELETE
UPDATE
MULTIREAD
Short Introduction to Structured Query Language (SQL)
SELECT
DELETE
INSERT
Designer View: Screen1
Blocks Code: Screen1
Designer View: Create
Blocks Code: Create
Designer View: Read
Blocks Code: Read
Designer View: Delete
Blocks Code: Delete
Designer View: Update
Blocks Code: Update
Designer View: MultiRead
Blocks Code: MultiRead
14 – Using Text Files in App Inventor
Source Code
Designer View
Blocks Code
Using CSV Format Files
The Super Easy Way to Import a CSV File
Where is testfile2.txt stored on your phone?
Using the AI 2 Companion
When Built as a .apk File
Step 1: Install File Manager
Step 2: Create a file folder to store your app data files
Step 3: Find the file!
Step 4: Sending the File to your computer
Step-by-step guide to Graphics, Animation and Charts
The App Inventor 2 guides introduce the fast and simple way to develop Android apps using MIT App Inventor, the software development system that runs in your browser to create apps that run on your smart phone and tablet.
Volume 4 introduces the use of graphics drawing features, including general graphics features, animation and charting. Charting refers to the creation of line, column and other types of charts commonly used in business and finance.
This book series is targeted at adult learners (high school or secondary school and up) who are interested in producing real world applications (rather than games). Hence, these books focus on features suitable for creating business, productivity and educational applications. Volume 4 assumes the reader is familiar with the basics of App Inventor programming; start with Volume 1 if you are new to App Inventor.
Each example provides code you can adapt or modify for use in your own programs so that you can create graphics, simple animation or charts in your own apps.
WHERE TO BUY
Please see the links at the top of this page.
Learn How To Create These Charts
Theory, design and sample code is provided for all of the following charts, plus more, including using sprites for animation, using “finger touch” to fling objects around the screen, using the accelerator and orientation sensor so that tilting the phone can control animation on screen.
Simple Line Chart
Simple Line Chart in Landscape Screen Orientation
Multiple Line / Data Series Charts
Line Chart With Regression Equation
Regression a way to find an equation that is the closest fit to the original data. Once the equation is calculated, the equation may then be used to draw a line across the chart showing predicted values.
Scatter Strip Chart
A scatter chart draws simple dots at the X, Y pair for each data element. A Scatter strip chart takes incoming data as a live data stream, and animates those points from right to left across the screen. New data points arrive at right, while the entire display of points scrolls to the left.
Strip Chart Recorder
This chart draws a line graph as new data arrives, at right. This type of chart might be in a heart monitor, for example, or in a voltage monitor that continuously monitors an input voltage. Data could arrive from a remote device over Bluetooth (such as from an Arduino board connected to sensors).
Use Image Picker
Animation Drawing – Wheel Rotates on Screen
The text shows how to create arbitrary animation in App Inventor apps. This wheel actually rotates as it moves across the screen.
Draw Column Charts
Table of Contents
ABOUT THIS BOOK
Web
Updates and Errata For this Book
Download Source Code for this Book
Disclaimer
About the Sample Apps and Blocks Code
Tip – Prevent the screen from rotating
Download Source Code
Video Tutorials
Conventions
INTRODUCTION TO GRAPHICS AND ANIMATED GAMES
In This Chapter
Video Tutorials for this Chapter
Bouncing Ball Animation-Ball1
Coordinate System
Selecting a Directional Heading
Coordinate System and Heading Summary
Ball1 – The User Interface
Source Code File
Designer View
Blocks Code
Ball2 – Using Sliders for Speed and Heading
Source Code
Designer View
Blocks Code
Ball3 – Adding a 2nd Ball
Source Code
Designer View
Blocks Code
Ball4 – Detecting Collisions
Source Code
Designer View
Blocks Code
Ball5 – Adding a Finger Touch Response
Source Code
Designer View
Blocks Code
IMAGE SPRITES
In This Chapter
Video Tutorials for this Chapter
The User Interface
Designer View
Blocks Code
Remove the Original Ball1 Object
Full Blocks Code
Where does the name “Sprite” come from?
Using Finger Touch to Control the Sprite Movement
Source Code
Designer View
Blocks Code
ORIENTATOIN SENSOR
In This Chapter
Video Tutorials for this Chapter
What the Sample Program Does
Tip: Turn off Auto-Rotate on your phone
Source Code
Designer View
Introduction to the Orientation Sensor
Blocks Code for Using the Orientation Sensor
How the Orient Button Works
Full Blocks Code
THE CANVAS
In This Chapter
Video Tutorials for this Chapter
Source Code
Introduction to the Canvas
User Interface
Designer View
Blocks Code
Picking and Saving Images
Flip: Multiple Canvases
ANIMATION METHODS
In This Chapter
Video Tutorials for this Chapter
Or scan this QR code
Animating Images
Source Code
User Interface
Designer View
Blocks Code
Using Multiple Images to Create Animated Subjects
Source Code
User Interface
Designer View
Blocks Code
Using a Sprite to Create an Animated Wheel That Moves
Source Code
User Interface
Designer View
Blocks Code
Using Multiple Canvas Objects for Animation
Source Code
User Interface
Designer View
Blocks Code
LINE CHARTS
In This Chapter
Video Tutorials for this Chapter
Source Code
User Interface
Designer View
Blocks Code
Scaling the Data
Line Charts With More than One Data Series
Global Variables
Data Initialization
Button Event Handlers
DrawEntireChart
Remaining Procedures are Unchanged
COLUMN CHARTS
In This Chapter
Video Tutorials for this Chapter
Source Code
User Interface
Designer View
Blocks Code
Initialization
Button Event Handlers
Chart Drawing
Scale Data
Draw X, Y Axis and Chart Title
DrawBox and DrawSolidBox Support Procedures
Using DrawLine to Draw a Rectangle
SCATTER PLOT CHART
In this Chapter
Video Tutorials for this Chapter
Source Code
User Interface
Designer View
Blocks Code
Initialization
Event Handlers
Drawing the Chart
Scaling the Data
DrawBox, X and Y Axes and Title
SCATTER PLOT WITH REGRESSION
In this Chapter
Video Tutorials for this Chapter
Source Code
User Interface
Designer View
Blocks Code
Initialization
Event Handlers
Drawing the Entire Chart
Calculating the Regression Equation
STRIP CHART RECORDER
In this Chapter
Video Tutorials for this Chapter
Source Code
User Interface
Designer View
Components List
Blocks Code
Initialization
Event Handlers
Data Generation
DrawBox, X and Y Axes and Title
STRIP CHART LINE RECORDER USING CANVAS FLIPPING
Video Tutorials for this Chapter
User Interface
Source code
Designer View
Blocks View
WHERE TO BUY
Please see the links at the top of this page.
Related Posts:
WiFi Manager Extension
See the App Inventor Extensions document about how to use an App Inventor Extension.
For questions about this extension or bug reports please start a new thread in the App Inventor Extensions forum. Thank you.
For feature requests please contact me by email. To be a sponsor of a new method already is possible starting from only 10 USD! With your contribution you will help the complete App Inventor community. Thank you.
Dec 22th, 2015: Version 1: initial release.
July 7th, 2016: Version 2: macAddress method added.
Aug 11th, 2016: Version 2a: avoid DX execution failed error: build each extension separately
Nov 27th, 2016: Version 3: BSSID method added
Feb 25th, 2017: Version 3a: bugfix IllegalArgumentException: Receiver not registered: null while switching screens
May 10th, 2017: Version 3b: bugfix IllegalArgumentException: Receiver not registered while switching screens
Aug 14th, 2017: Version 4: correspondingRSSIs, SignalStrength, ConnectionInfo, Is5GHzBandSupported added
Aug 16th, 2017: Version 5: correspondingBSSIs added
Dec 6th, 2017: Version 5a: bugfix configuredSSIDs, see also here. Thank you Edgar for the error report.
Dec 14th, 2017: Version 5b: bugfix ConnectSSID, see also here. Thank you again Edgar for the error report.
App Inventor 2 Download Windows
Apr 8th, 2018: Version 6: new method AccessPointIP added
Apr 13th, 2018: Version 7: connect without password
Aug 29th, 2018: Version 8: Disconnect method added
Nov 6th, 2018: Version 9: Dnsservers method added
Jan 23th, 2019: Version 10: SDK 26 update: dangerous permission android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION removed. What is a dangerous permission? The method AvailableSSIDs including its corresponding event have been removed.
Jan 28th, 2019: Version 11: AvailableSSIDs added again. Additionally example project provided about how to use it together with the location sensor and GPS enabled.
Oct 21th, 2019: Version 12: AfterWifiNegotiation event added
Oct 21th, 2019: Version 13: RemoveSSID added
Oct 21th, 2019: Version 14: LocalIP: returns wifi ip if its enabled else the cellular one
Description
Some useful blocks to use in a wireless lan.
Required permissions: android.permission.ACCESS_WIFI_STATE, android.permission.CHANGE_WIFI_STATE
Properties
Returns whether Success Message should be suppressed.
Specifies whether Success Message should be suppressed.
Returns whether Warning Message should be suppressed.
Specifies whether Warning Message should be suppressed.
Methods

Return the local IP Address. Returns wifi ip if its enabled else the cellular one.
Sponsor of this block is Marius. Thank you!
Return the MAC Address of the device.
Sponsor of this block is Niko. Thank you!
Get current WiFi state: true or false.
Enable WiFi.
You can hide the success message after setting the suppressSuccessMessage property to false.
Note: to be able to test this block, you have to build the app, because the permission CHANGE_WIFI_STATE is not available in the companion app.
Note: starting from Android 10, this method does not work anymore, see also this stackoverflow answer. For Android 10 you might want to try this Activity Starter solution.
Disable WiFi.
You can hide the success message after setting the suppressSuccessMessage property to false.
Note: to be able to test this block, you have to build the app, because the permission CHANGE_WIFI_STATE is not available in the companion app. Note: starting from Android 10, this method does not work anymore, see also this stackoverflow answer.
Get current WiFi SSID (Service Set Identifier).
Note; Starting with Android 8.1 (API 27), apps must be granted the ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION (or ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION) permission in order to obtain the SSID or BSSID. Apps that target API 29 or higher (Android 10) must be granted ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION. See also this stackoverflow answer.
Therefore just drag a location sensor component into your project and additionally ask for permission ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION.
Get current WiFi BSSID (the MAC address of the access point).
Thank you burrowmoor for being the sponsor of this method.
Note; Starting with Android 8.1 (API 27), apps must be granted the ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION (or ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION) permission in order to obtain the SSID or BSSID. Apps that target API 29 or higher (Android 10) must be granted ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION. See also this stackoverflow answer.
Therefore just drag a location sensor component into your project and additionally ask for permission ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION.
Connect to a SSID (Service Set Identifier).
If you provide a non existing SSID or wrong password, this just will be ignored and the device will try to connect to a known SSID instead.
Note: Starting from version 7 it is also possible to connect to an open network, i.e. a SSID, which does not have a password. Thank you Robert for being the sponsor of this enhancement.
Note: to be able to test this block, you have to build the app, because the permission CHANGE_WIFI_STATE is not available in the companion app.
Get a list of configured SSIDs (Service Set Identifiers). WiFi must be enabled for this.
Get a list of available SSIDs (Service Set Identifiers). WiFi must be enabled for this.
Note: to be able to test this block, you have to build the app, because the permission CHANGE_WIFI_STATE is not available in the companion app.
Note: Precondition to use this method is to add a location sensor component into your project. Also GPS must be enabled. See the example project about how to use it.
Get current connection info.
For details, see also WiFiInfo documentation.
Download version 9.51 of Total Commander (fully functional Shareware version, 5MB EXE file). Parallels or Crossover for Mac to use Total Commander on an Apple Mac computer. Or try Commander One - Free File Manager for Mac OS X with PRO Pack of additional features for advanced file management. Aimed to be an alternative of Total Commander. Total commander mac download.
Check, if 5 GHz Band is supported. Returns true or false.
Get signal strength (RSSI) in a range between 0 and 100.
This algorithm is used to calculate the signal strength.
Get IP address of the access point.
Thank you Eric for being the sponsor of this method.
Disconnect.
Note: after disconnecting the device might reconnect automatically to the next available known network.
Thank you Wei Zheng for being the sponsor of this method.
Return a list of DNS servers (primary and secondary) of the current network.
Note: The method returns the IP address of the gateway router when DNS is not configured inside the router.
Thank you Gabriel for being the sponsor of this method.
Remove a SSID from the network list. Note: starting from Android M, apps are not allowed to remove networks that they did not create.
Events
Event indicating that Available SSIDs (Service Set Identifiers) have been scanned.
A list of the available SSIDs is provided in parameter availableSSIDs. The SSID having the best signal is provided in parameter bestSSID. A list of the corresponding RSSIs is provided in parameter correspondingRSSI. A list of corresponding BSSIs is provided in parameter correspondingBSSIs.
Thank you Tal for being the sponsor of the correspondingRSSI and correspondingBSSI functionality.
Check if the negotiation with the WifiConfiguration was successful, Returns true or false.
Example App: WiFi Test
Example App: Get Available SSIDs
App Inventor Download Windows 10
Note: Precondition to use the AvailableSSID method is
- to add a location sensor component into the project
- to enable GPS and
- to build the app to test its functionality
Screenshot
Test
Tested successfully on Samsung Galaxy A5 (2017) running Android 8.0.
Questions and Answers
App Inventor 2 Ultimate Download
Q1: Please check TaifunWiFi.SSID in Android 9. When I build it with Android 9 (Samsung S9), the result of TaifunWiFi.SSID is <unknown ssid>. But, if I build it with Android 5, the TaifunWiFi.SSID works well. Thank you.
A: You might want to try the example project 'Get Available SSIDs' downloadable from the download section below, which adds a location sensor into the project to get the permission ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION. Additionally please enable GPS and try using the method SSID again for Android 9 devices. See also here.
For questions about App Inventor,
please ask in the App Inventor community.Thank you.
Terms and Conditions
- Have fun and use this extension in your App Inventor projects! Pura Vida!
- THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED 'AS IS', WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
- This is is the only authorized place to download this extension. It is not allowed to host this extension somewhere else and offer it for others to download, be it on another website or market place or similar. The reason is, everybody should be able to have the opportunity to donate something in case you like my work. You are allowed to provide a link to this site, so others can download the extension here. You will find the most up to date version always here including documentation and usage examples. Thank you for your kind understanding.
Download App Inventor Full
Download
Developing and maintaining snippets, tutorials and extensions for App Inventor takes a lot of time.
I hope it saved some of your time. If yes, then you might consider to donate a small amount!
App Inventor 2 Download Mac Os
or donate some mBTC to Address:
1Jd8kXLHu2Vkuhi15TWHiQm4uE9AGPYxi8
Thank you! Taifun
Download TaifunWiFi extension (aix file)
Download WiFi Test (aia file)
Download Available SSIDs Test (aia file)
Back to top of page ..
App Inventor 2 Download Mac Installer
This work by Pura Vida Apps is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License
with attribution (name=Pura Vida Apps and link to the source site) required.

